
In 1800, German-born British astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel was experimenting to measure the temperature within the colour range of sunlight. He directed sunlight through a glass prism to create a rainbow-like spectrum.
From blue to red there was an increase in temperature but beyond the visible light spectrum, right after the red end, the thermometer displayed the highest temperature.
This was infrared light or infrared radiation (IR), a type of electromagnetic radiation that’s invisible to the eye but is felt as heat. We can only “see” it through infrared and thermal cameras.
Infrared Radiation Categories
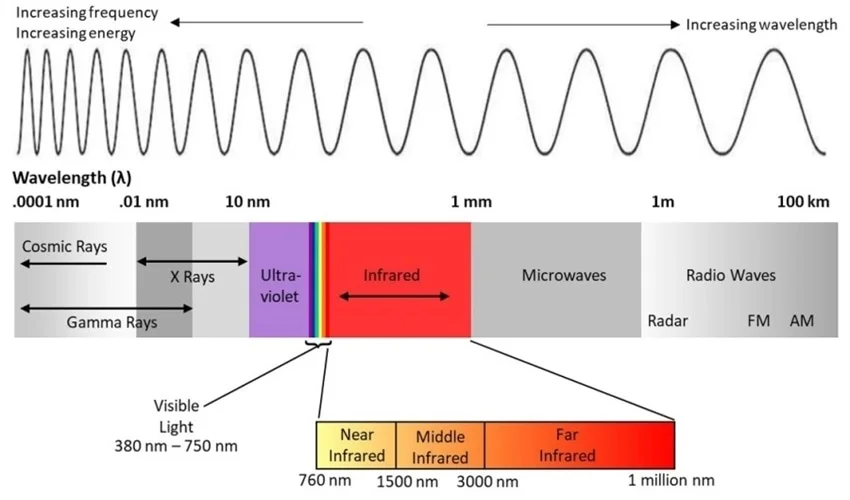
Like the visible light spectrum, infrared radiation has its own range of regions or bands, based on wavelengths. The shorter frequency waves closer to the visible light are the “near-infrared waves” that don’t emit any detectable heat. They generally consist of 750 nm to 1,300 nm wavelengths. This is what a remote control uses to change the channels.

Then there’s the mid IR band which has a wavelength range of about 1,300 nm to 3,000 nm.
The third region or the longer “far-infrared waves” closer to the right end of the electromagnetic spectrum can be felt as intense heat. Its wavelength ranges from 3,000 nm to 1 mm. Common sources are the sun and fire. Even the human body at 37°C can give off infrared radiations of around 800 nm wavelength.
From these three bands, IR can also be divided into five subcategories: near-wavelength, short-wavelength, mid-wavelength, long-wavelength, and far-infrared. The total spectrum has a wavelength range of about 700 nm to 1 mm.
Uses of Infrared Radiation
Infrared radiation usually goes unnoticed but it’s something you encounter every day. Toasters, incandescent bulbs, and remote controls use infrared energy, as well as industrial heaters used in drying and curing materials.
For medical uses, infrared radiation is a heating source in saunas as a sort of physiotherapy to treat high blood pressure and arthritis. It’s important to note, though, that infrared saunas could be harmful for those with melasma or other skin pigmentation issues.

Another useful application of infrared radiation is detection. Night vision goggles use thermal imaging exposing objects or people emitting heat in the form of infrared. It’s also used in non-contact thermometers.

In astronomy, infrared radiation has led to the discovery of comets, asteroids, and dust clouds. It helps in detecting objects that are too cold to be observed in visible light and light from the early Universe that has shifted into the infrared spectrum.
An example of infrared equipment is the Infrared Array Camera (IRAC) which was in the Spitzer Space Telescope launched in 2003. IRAC was one of Spitzer’s science instruments. It was a four-channel camera that provided wide-field images and guided studies on star and planet formation, exoplanets, and galaxies.
Real-Time Radiation Monitoring
Radiation has useful applications in various industries. To use it in its full potential, we should also practise safety and avoid unnecessary radiation exposure.
Looking for area radiation monitors or personal radiation monitoring devices? You can count on SensaWeb. With our monitors, you can easily detect and interdict radioactive materials. Connect with us here or at our email address: info@sensaweb.com.au. You can also call us at +61 415 409 467.